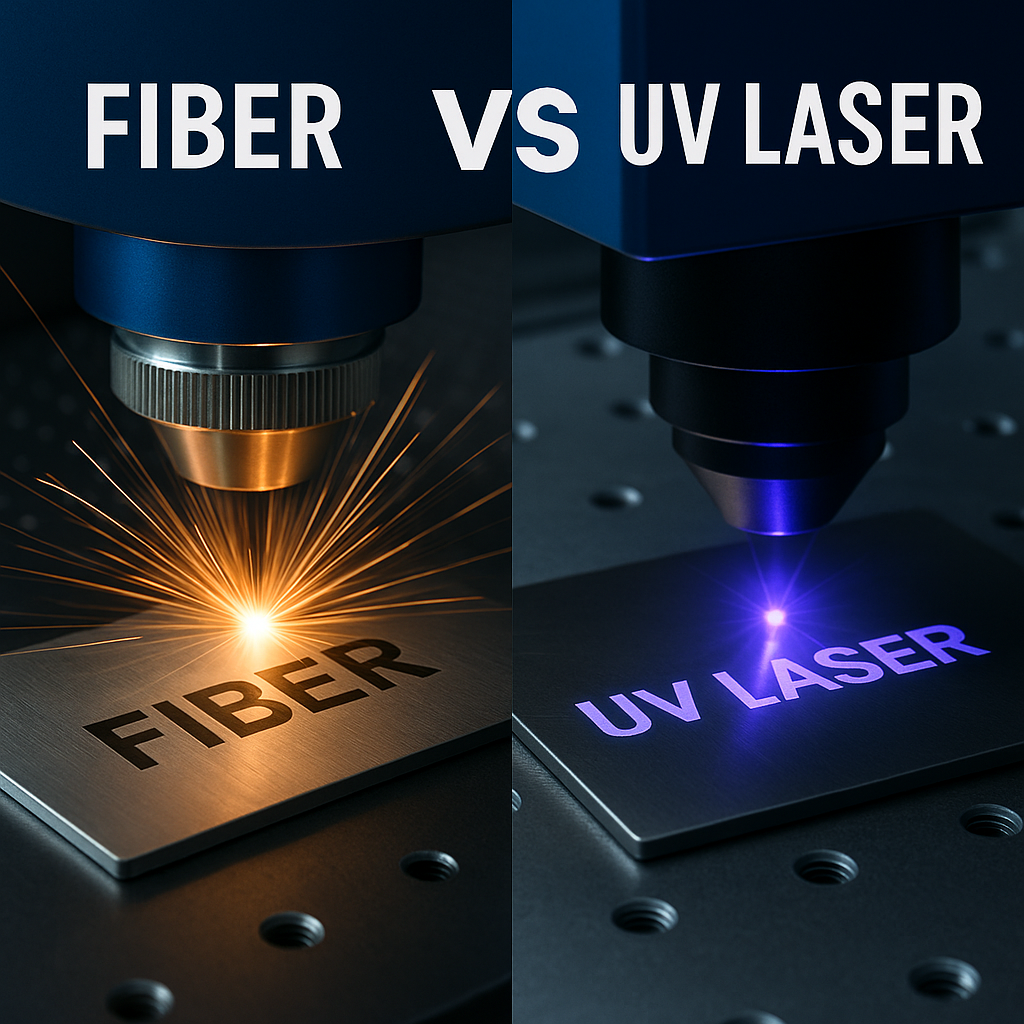
Fiber Laser vs UV Laser Engraving: Key Differences Explained
Choosing between a fiber laser and UV laser engraver feels like picking between Thor’s hammer and a surgeon’s scalpel. Short answer: fiber lasers dominate metals, while UV laser engravers excel on delicate materials like glass and plastics. Keep reading to see which one’s the perfect fit for your projects.

Fiber Laser vs. UV Laser: A Core Technology Comparison
Think of fiber and UV lasers like two very different tools in the same workshop. Both are powerful, both are precise, but they shine in different situations. The trick is knowing which one fits your job best.
How Each Laser Works
The Operating Principle of a Fiber Laser
Fiber lasers are the heavy hitters. They generate a beam at around 1060 nm wavelength, which metals absolutely love. The energy digs deep into the surface, creating marks that last and cuts that go straight through. That’s why industries rely on them for stainless steel, aluminum, and other alloys.
The "Cold Marking" Process of a UV Laser
UV lasers, on the other hand, take the gentle route. Working at 355 nm wavelength, they don’t burn or melt the surface. Instead, the energy stays right on top, leaving behind sharp marks without warping the material. It’s why people call it “cold marking” — the detail is stunning, and the material stays intact.
Key Wavelengths and Their Impact
Wavelength is the real game changer. Fiber lasers, with their infrared wavelength, excel at metals because that’s where absorption is strongest. UV lasers, with their shorter wavelength, thrive on delicate stuff — plastics, glass, even paper. One is the hammer, the other is the scalpel.
Material Compatibility: The Primary Difference
If you only remember one thing, make it this: fiber lasers are built for metals, UV lasers are built for delicate materials.

Fiber Laser: The "Metal Specialist"
Best for Deep Engraving and Cutting Metals
Need to etch a serial number into an engine block? A fiber laser can do that all day long. From industrial tooling to jewelry engraving, these machines handle deep, durable marks that hold up under stress.
Performance on Certain Plastics
Yes, fiber lasers can engrave some plastics — but results aren’t always consistent. They’re not the go-to for polymers when detail and clarity matter most.
UV Laser: The "Delicate Material Master"
Unmatched for Glass and Crystal
Glass and lasers usually don’t mix well. But UV lasers break the rules. They can engrave frosted patterns on wine glasses, etch logos on crystal awards, and even mark glass components in electronics — all without cracks or breakage.
Superior Results on Plastics and Polymers
Plastics melt under heat, but not under UV. From ABS casings in electronics to medical-grade polymers, UV lasers engrave without leaving burn marks. The results are crisp and professional.
Performance on Organic Materials
Cardboard packaging, leather wallets, even high-end stationery — UV lasers mark them cleanly without singeing. It’s why they’re popular in creative industries as much as in manufacturing.
Performance Metrics and Use Cases

Speed and Efficiency
Fiber lasers are built for speed. On a production line engraving thousands of parts, they cut time dramatically. UV lasers, while slower, make up for it with unmatched detail.
Engraving Precision and Spot Size
Here’s where UV wins big. With a smaller spot size, it can engrave QR codes smaller than a grain of rice. Fiber lasers are precise too, but they’re built more for strength and durability than for micro-detail.
Impact on the Material (Heat-Affected Zone)
Fiber lasers create a bigger heat-affected zone because metals demand more energy. UV lasers keep heat to a minimum, which is exactly what makes them so good on fragile materials.
Common Applications and Industries
Industrial and Automotive (Fiber)
Fiber lasers dominate here. Think of part numbers on auto components, durable branding on tools, or high-speed cutting of sheet metal.
Medical Devices and Electronics (UV)
UV lasers thrive in industries where detail is everything. They etch calibration marks on syringes, serial numbers on surgical tools, and high-contrast IDs on circuit boards.
Cost, Maintenance, and Longevity
Initial Purchase Price Comparison
Fiber lasers usually carry a bigger upfront price tag, especially high-power units. UV lasers often start lower, but pricing can climb depending on the machine’s precision and capabilities.
Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
Fiber lasers are famously long-lived, often running tens of thousands of hours before major servicing. UV lasers, while powerful in their niche, tend to need more frequent calibration and upkeep.
Operational Costs
For heavy-duty metal work, fiber lasers pay for themselves with efficiency and low operating costs. UV lasers may cost more to maintain, but their ability to handle sensitive, high-value materials makes them indispensable in fields like medical devices and luxury goods.
Final Thoughts
Choosing between a fiber and a UV laser isn’t about which one is “better.” It’s about which one is better for you. If your work lives in the world of metals, fiber is the obvious winner. If you need flawless precision on glass, plastics, or electronics, UV is the clear choice.
Leave a comment