What Can a UV Laser Engraver Do?
Ever wondered if UV Laser Engravers are magic wands in disguise? Short answer: they etch metals, plastics, glass, and more with mind-blowing precision. From jewelry to circuit boards, their versatility is unmatched—stick around to discover why industries everywhere are hooked on these laser-powered superheroes.

What is a UV Laser Engraver?
Think of a UV laser engraver as the artist in the laser family. Instead of brute force cutting, it’s designed for finesse — creating tiny, precise marks where detail really matters.
Unlike other lasers, a UV system doesn’t rely on high heat to do its work. That’s why it’s often called a “cold” laser. The result? Clean, sharp engravings without scorch marks, cracks, or unwanted burns.

The "Cold Marking" Process
Here’s where the magic happens. A UV laser works at a short wavelength — around 355 nm — which is absorbed quickly by many different materials.
Instead of heating the surface until it melts, the laser energy disrupts the molecular bonds directly. This process leaves behind a crisp, permanent mark while the rest of the material stays cool and intact. It’s the secret sauce for working with fragile items like plastics, glass, or thin films.
Key Characteristics and Technology
A UV laser engraver is made up of three core parts: the laser source itself, a control system, and a precision movement system. Together, they deliver accuracy down to fractions of a millimeter.
In practice, this means you can engrave things as delicate as serial numbers on microchips or as bold as a logo on a medical device. The technology is built for detail — not brute force cutting — and that’s what sets it apart.
What Can a UV Laser Engraver Do? – Key Applications and Materials

High-Precision Engraving and Marking
If you’ve ever squinted at the tiny lettering on the back of your phone or the codes on a circuit board, chances are you’ve seen a UV laser’s handiwork. These machines are built for that kind of precision.
They can engrave logos, barcodes, QR codes, or intricate artwork so small you’d need a magnifying glass to appreciate it.
Marking on Heat-Sensitive Materials
Heat-sensitive surfaces are where UV lasers shine. Plastics that would normally melt under a fiber or CO₂ laser stay perfectly intact.
Think of things like medical syringes, electronic casings, or even consumer packaging. The marks are durable, but the material itself doesn’t suffer.
Marking a Wide Range of Materials
UV lasers aren’t picky. Metals, polymers, glass, ceramics, coated surfaces — you name it, they can handle it.
This versatility makes them a go-to tool across multiple industries where a single project may involve very different materials.
What Materials Can a UV Laser Engrave?
Plastics and Polymers
UV lasers engrave plastics cleanly, with no yellowing or melted edges. That’s why they’re used so often in electronics, where housings and connectors need clear, permanent marks.
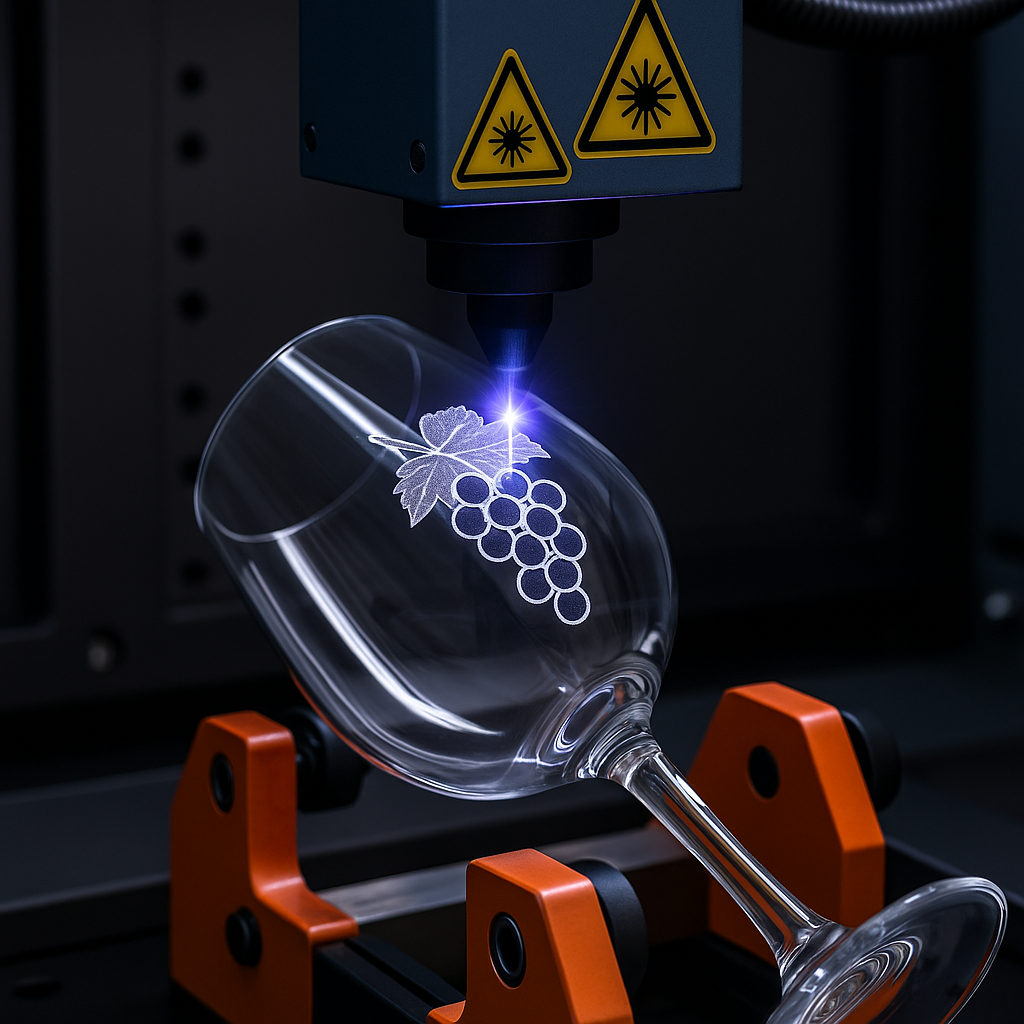
Glass and Crystal
Imagine a wine glass with a custom logo etched so fine it looks like it came from a luxury brand. Or glass components in electronics where clarity and durability are critical. UV lasers make both possible.
Metals and Coated Metals
While fiber lasers do the heavy lifting with metals, UV lasers specialize in detailed surface marking. Anodized aluminum, stainless steel with coatings, or plated jewelry can all be marked without compromising the finish.
Organic and Delicate Materials
Paper, leather, even delicate films can be marked with surprising precision. Brands use this for packaging, luxury goods, and high-end stationery where every detail matters.

UV Lasers in Different Industries
Electronics and Semiconductors
In electronics, size matters — and smaller is better. UV lasers mark tiny PCBs, chips, and micro-components with codes that must remain readable for years. Without UV lasers, managing traceability in this sector would be a nightmare.
Medical Devices
Surgical tools, implants, and instruments often require permanent markings for identification and compliance. UV lasers can do this without leaving residue or damaging the integrity of the device. It’s accuracy you can literally bet a life on.
Automotive and Aerospace
Engines, gear components, and aircraft parts all need durable serial numbers and identification marks. UV lasers deliver these quickly and clearly, ensuring parts can be traced back through their entire life cycle.
Jewelry and Luxury Goods
In jewelry, detail is everything. UV lasers let jewelers etch initials, logos, or designs onto metals and gemstones with flawless precision. Luxury brands use them for personalization without risking damage to premium materials.
UV Laser Engraver: A Comparison with Other Laser Types
UV Laser vs. Fiber Laser
Fiber lasers are the muscle of the group, ideal for deep engraving in metals. But they don’t play well with plastics or glass.
UV lasers, on the other hand, are the detail specialists. They excel where fiber lasers would simply overheat or damage the material.
UV Laser vs. CO2 Laser
CO₂ lasers are fantastic for cutting and engraving organics like wood, acrylic, and leather. But when it comes to ultra-fine marking on plastics, glass, or electronics, UV lasers take the crown. They fill a gap CO₂ lasers just can’t reach.
Is a UV Laser Engraver Right for You?
Key Benefits of UV Laser Engraving
-
Incredible precision and micro-marking ability.
-
Handles fragile and coated surfaces with ease.
-
Leaves permanent, high-contrast results.
-
Versatile enough for both industrial and creative uses.
Considerations for Your Business or Hobby
UV laser engravers are an investment. They typically cost more than CO₂ or diode machines, but you’re paying for precision and versatility.
If your focus is on cutting wood or acrylic, a CO₂ laser may be a better fit. But if you need to engrave sensitive plastics, detailed electronics, or luxury items, a UV laser engraver is absolutely worth considering.

Leave a comment